مدونة الموقع
اتصل بنا
- إذا كانت لديك أسئلة، يرجى الاتصال بنا، وسيتم الرد على جميع الأسئلة
- البريد الإلكتروني : David@tmaxcn.com
- البريد الإلكتروني : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- إضافة : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
المنتجات الساخنة
مدونة
Dry Electrode Preparation Solution
December 27,2024.
Dry Electrode Preparation Solution: A Key to Sustainable and Efficient Battery Manufacturing
The dry electrode preparation solution is an innovative approach in the field of battery manufacturing, particularly for lithium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries. Traditional electrode fabrication techniques involve the use of solvents to prepare the slurry for coating onto electrodes. However, the dry electrode preparation method eliminates the need for solvents, making it more environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and efficient.
This article explores the dry electrode preparation process, its advantages, the technology behind it, and how it is transforming the battery manufacturing landscape.
---
● What is Dry Electrode Preparation?
Dry electrode preparation refers to the process of creating battery electrodes (typically made from active materials like lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), nickel cobalt manganese (NCM), or graphite) without using solvents, which are commonly used in conventional slurry-based electrode manufacturing.
In the dry process, the active materials, conductive additives, and binders are mixed in their solid forms and then processed to form the electrode. The resulting electrode is then coated directly onto a substrate, such as copper foil for the anode or aluminum foil for the cathode, using advanced techniques like dry rolling, lamination, or pressure application.
---
● Why is Dry Electrode Preparation Important?
The dry electrode preparation method offers a number of significant advantages over the conventional wet slurry approach, which can help streamline production, improve sustainability, and lower costs.
1. Environmental Benefits
- Eliminates Solvent Use: Traditional wet electrode preparation involves toxic solvents such as N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), which not only poses health and safety risks but also requires specialized equipment for disposal and recycling. The dry method eliminates the need for these solvents, making the process more environmentally friendly.
- Reduced Emissions: By not using volatile solvents, the dry electrode process reduces harmful emissions and minimizes the environmental footprint of battery production.
2. Cost Reduction
- Lower Material and Energy Costs: The dry electrode process eliminates the need for costly solvents, slurry preparation, and drying steps, reducing both material costs and energy consumption.
- Simplified Production: The absence of a solvent-based slurry and drying process simplifies the overall production line, reducing equipment complexity and maintenance costs.
3. Increased Energy Density
- Higher Active Material Loading: Without the need for solvents or drying processes, the electrode materials can be packed more densely, leading to higher energy density and better overall battery performance.
- Reduced Binder Content: The dry method typically uses less binder material compared to the wet method, allowing for more active material to be used in the electrode, thus improving capacity and energy density.
4. Faster and More Efficient Production
- Faster Manufacturing Cycle: Since the dry electrode preparation process does not require lengthy drying steps, it significantly speeds up the production process, improving throughput and reducing cycle time in the factory.
- Less Waste: The dry process is more efficient, generating less waste compared to the traditional wet process, which often requires the disposal of excess slurry.
---
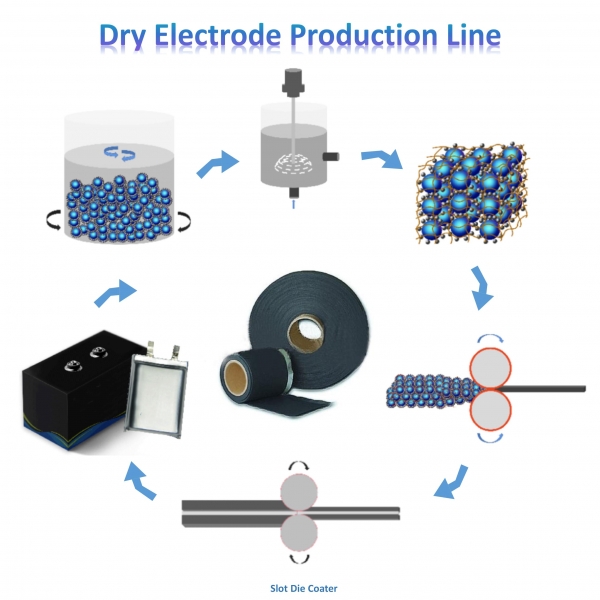
● How Does the Dry Electrode Preparation Process Work?
The dry electrode preparation process typically involves several key steps:
1. Material Mixing
- In the dry electrode method, active materials, conductive additives (like carbon black or graphene), and binders are mixed in their dry powder form. Special attention is paid to achieving uniform dispersion of the particles, which is crucial for maximizing the conductivity and performance of the electrode.
2. Compression and Forming
- The mixed powders are then compressed to form a solid, cohesive material. This is typically done using techniques such as dry rolling, lamination, or extrusion. The compressed material is then coated directly onto a conductive metal substrate, typically aluminum (for the cathode) or copper (for the anode), to form the electrode.
3. Electrode Coating
- The solid, dry mixture is applied to the substrate using methods such as direct dry coating, where the electrode material is spread evenly onto the foil. This step requires precision to ensure uniform thickness and adhesion to the metal substrate.
4. Pressure Application
- After coating, the electrode may undergo a pressure application step (such as calendaring or compression) to achieve the desired electrode thickness and density. This step helps to ensure a high-quality electrode with optimal performance characteristics.
5. Drying (Optional)
- While traditional slurry-based processes require extensive drying to evaporate solvents, the dry electrode method usually does not require any drying, as there are no solvents involved. However, in some cases, the electrodes may undergo light heating or curing to ensure the binder fully bonds the active materials.
6. Final Inspection and Testing
- Once the electrode is produced, it undergoes rigorous quality control checks and testing to ensure the electrode's performance, including its capacity, resistance, and cycle life. These tests are vital to confirm that the electrode meets the necessary standards for energy storage and durability.
---
● Key Technologies Behind Dry Electrode Preparation
Several innovative technologies are enabling the dry electrode preparation process to become more viable and scalable for commercial production:
1. Roll-to-Roll (R2R) Technology
- Roll-to-roll technology is commonly used in dry electrode production. It involves feeding continuous rolls of metal foil and dry electrode material through rollers or presses, allowing for large-scale production of electrodes with uniform thickness. This technique is fast, scalable, and ideal for high-volume battery manufacturing.
2. Laser Sintering
- Laser sintering is a process that uses lasers to fuse dry particles together into a solid structure without the need for solvents or external heat. This can be used to create highly efficient, durable electrodes with precise control over the material structure.
3. High-Energy Ball Milling
- Ball milling is often employed to mix and refine the dry powder materials, improving the consistency and quality of the electrode mixture. This technology helps achieve uniform particle size distribution, which is crucial for ensuring optimal electrochemical performance.
4. Electrostatic or Mechanical Coating
- In some cases, electrostatic or mechanical coating techniques are used to apply dry powder directly onto the metal substrate, ensuring an even layer of electrode material without the need for solvents.
---
● Challenges and Limitations of Dry Electrode Preparation
While the dry electrode preparation method offers significant advantages, there are still some challenges and limitations to consider:
1. Material Handling and Dispersion:
- Achieving uniform dispersion of dry powders can be challenging, as the materials must be carefully mixed to avoid agglomeration and ensure consistent performance. Specialized equipment is often required for this step.
2. Lower Binder Efficiency:
- The binder used in the dry electrode process may not be as effective in certain applications compared to solvent-based processes, potentially leading to reduced adhesion or performance. Ongoing research is focused on developing better binders for dry processing.
3. Limited Compatibility with Some Materials:
- Certain battery chemistries or advanced materials may not be as compatible with the dry electrode process. For example, some high-energy cathode materials may require more complex preparation methods that involve solvents to ensure proper electrode formation.
4. Scaling Challenges:
- While dry electrode preparation is promising on a small scale, scaling it up to meet the demands of mass production is still a work in progress. The technology is rapidly advancing, but it may take time to overcome the challenges of fully automating the process at industrial scale.
---
● The Future of Dry Electrode Preparation
The Dry Electrode Manufacturing Line is poised to revolutionize the battery manufacturing industry, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional solvent-based methods. As the demand for high-performance, environmentally-friendly batteries continues to grow, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage markets, the adoption of dry electrode technologies is expected to accelerate.
In the future, we can expect to see:
- Wider adoption of dry electrode processes across various battery chemistries, including solid-state batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and lithium-ion batteries.
- Increased efficiency and automation in manufacturing lines, improving scalability and consistency in dry electrode production.
- Continued advancements in materials science, leading to better binders, conductive additives, and electrode materials tailored for dry processing.
- Lower costs and reduced environmental impact, making dry electrode technology an attractive choice for large-scale commercial production.
---
● Conclusion
The dry electrode preparation solution is a cutting-edge advancement in the battery manufacturing process, offering significant benefits in terms of sustainability, cost, and efficiency. By eliminating the need for solvents and complex drying steps, it promises to make battery production more environmentally friendly, faster, and cost-effective, all while maintaining or improving battery performance. As the industry moves towards more sustainable and scalable manufacturing methods, the dry electrode process will play a critical role in shaping the future of energy storage technologies.
The dry electrode preparation solution is an innovative approach in the field of battery manufacturing, particularly for lithium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries. Traditional electrode fabrication techniques involve the use of solvents to prepare the slurry for coating onto electrodes. However, the dry electrode preparation method eliminates the need for solvents, making it more environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and efficient.
This article explores the dry electrode preparation process, its advantages, the technology behind it, and how it is transforming the battery manufacturing landscape.
---
● What is Dry Electrode Preparation?
Dry electrode preparation refers to the process of creating battery electrodes (typically made from active materials like lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), nickel cobalt manganese (NCM), or graphite) without using solvents, which are commonly used in conventional slurry-based electrode manufacturing.
In the dry process, the active materials, conductive additives, and binders are mixed in their solid forms and then processed to form the electrode. The resulting electrode is then coated directly onto a substrate, such as copper foil for the anode or aluminum foil for the cathode, using advanced techniques like dry rolling, lamination, or pressure application.
---
● Why is Dry Electrode Preparation Important?
The dry electrode preparation method offers a number of significant advantages over the conventional wet slurry approach, which can help streamline production, improve sustainability, and lower costs.
1. Environmental Benefits
- Eliminates Solvent Use: Traditional wet electrode preparation involves toxic solvents such as N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), which not only poses health and safety risks but also requires specialized equipment for disposal and recycling. The dry method eliminates the need for these solvents, making the process more environmentally friendly.
- Reduced Emissions: By not using volatile solvents, the dry electrode process reduces harmful emissions and minimizes the environmental footprint of battery production.
2. Cost Reduction
- Lower Material and Energy Costs: The dry electrode process eliminates the need for costly solvents, slurry preparation, and drying steps, reducing both material costs and energy consumption.
- Simplified Production: The absence of a solvent-based slurry and drying process simplifies the overall production line, reducing equipment complexity and maintenance costs.
3. Increased Energy Density
- Higher Active Material Loading: Without the need for solvents or drying processes, the electrode materials can be packed more densely, leading to higher energy density and better overall battery performance.
- Reduced Binder Content: The dry method typically uses less binder material compared to the wet method, allowing for more active material to be used in the electrode, thus improving capacity and energy density.
4. Faster and More Efficient Production
- Faster Manufacturing Cycle: Since the dry electrode preparation process does not require lengthy drying steps, it significantly speeds up the production process, improving throughput and reducing cycle time in the factory.
- Less Waste: The dry process is more efficient, generating less waste compared to the traditional wet process, which often requires the disposal of excess slurry.
---
● How Does the Dry Electrode Preparation Process Work?
The dry electrode preparation process typically involves several key steps:
1. Material Mixing
- In the dry electrode method, active materials, conductive additives (like carbon black or graphene), and binders are mixed in their dry powder form. Special attention is paid to achieving uniform dispersion of the particles, which is crucial for maximizing the conductivity and performance of the electrode.
2. Compression and Forming
- The mixed powders are then compressed to form a solid, cohesive material. This is typically done using techniques such as dry rolling, lamination, or extrusion. The compressed material is then coated directly onto a conductive metal substrate, typically aluminum (for the cathode) or copper (for the anode), to form the electrode.
3. Electrode Coating
- The solid, dry mixture is applied to the substrate using methods such as direct dry coating, where the electrode material is spread evenly onto the foil. This step requires precision to ensure uniform thickness and adhesion to the metal substrate.
4. Pressure Application
- After coating, the electrode may undergo a pressure application step (such as calendaring or compression) to achieve the desired electrode thickness and density. This step helps to ensure a high-quality electrode with optimal performance characteristics.
5. Drying (Optional)
- While traditional slurry-based processes require extensive drying to evaporate solvents, the dry electrode method usually does not require any drying, as there are no solvents involved. However, in some cases, the electrodes may undergo light heating or curing to ensure the binder fully bonds the active materials.
6. Final Inspection and Testing
- Once the electrode is produced, it undergoes rigorous quality control checks and testing to ensure the electrode's performance, including its capacity, resistance, and cycle life. These tests are vital to confirm that the electrode meets the necessary standards for energy storage and durability.
---
● Key Technologies Behind Dry Electrode Preparation
Several innovative technologies are enabling the dry electrode preparation process to become more viable and scalable for commercial production:
1. Roll-to-Roll (R2R) Technology
- Roll-to-roll technology is commonly used in dry electrode production. It involves feeding continuous rolls of metal foil and dry electrode material through rollers or presses, allowing for large-scale production of electrodes with uniform thickness. This technique is fast, scalable, and ideal for high-volume battery manufacturing.
2. Laser Sintering
- Laser sintering is a process that uses lasers to fuse dry particles together into a solid structure without the need for solvents or external heat. This can be used to create highly efficient, durable electrodes with precise control over the material structure.
3. High-Energy Ball Milling
- Ball milling is often employed to mix and refine the dry powder materials, improving the consistency and quality of the electrode mixture. This technology helps achieve uniform particle size distribution, which is crucial for ensuring optimal electrochemical performance.
4. Electrostatic or Mechanical Coating
- In some cases, electrostatic or mechanical coating techniques are used to apply dry powder directly onto the metal substrate, ensuring an even layer of electrode material without the need for solvents.
---
● Challenges and Limitations of Dry Electrode Preparation
While the dry electrode preparation method offers significant advantages, there are still some challenges and limitations to consider:
1. Material Handling and Dispersion:
- Achieving uniform dispersion of dry powders can be challenging, as the materials must be carefully mixed to avoid agglomeration and ensure consistent performance. Specialized equipment is often required for this step.
2. Lower Binder Efficiency:
- The binder used in the dry electrode process may not be as effective in certain applications compared to solvent-based processes, potentially leading to reduced adhesion or performance. Ongoing research is focused on developing better binders for dry processing.
3. Limited Compatibility with Some Materials:
- Certain battery chemistries or advanced materials may not be as compatible with the dry electrode process. For example, some high-energy cathode materials may require more complex preparation methods that involve solvents to ensure proper electrode formation.
4. Scaling Challenges:
- While dry electrode preparation is promising on a small scale, scaling it up to meet the demands of mass production is still a work in progress. The technology is rapidly advancing, but it may take time to overcome the challenges of fully automating the process at industrial scale.
---
● The Future of Dry Electrode Preparation
The Dry Electrode Manufacturing Line is poised to revolutionize the battery manufacturing industry, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional solvent-based methods. As the demand for high-performance, environmentally-friendly batteries continues to grow, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage markets, the adoption of dry electrode technologies is expected to accelerate.
In the future, we can expect to see:
- Wider adoption of dry electrode processes across various battery chemistries, including solid-state batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and lithium-ion batteries.
- Increased efficiency and automation in manufacturing lines, improving scalability and consistency in dry electrode production.
- Continued advancements in materials science, leading to better binders, conductive additives, and electrode materials tailored for dry processing.
- Lower costs and reduced environmental impact, making dry electrode technology an attractive choice for large-scale commercial production.
---
● Conclusion
The dry electrode preparation solution is a cutting-edge advancement in the battery manufacturing process, offering significant benefits in terms of sustainability, cost, and efficiency. By eliminating the need for solvents and complex drying steps, it promises to make battery production more environmentally friendly, faster, and cost-effective, all while maintaining or improving battery performance. As the industry moves towards more sustainable and scalable manufacturing methods, the dry electrode process will play a critical role in shaping the future of energy storage technologies.
 English▼
English▼




 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

