مدونة الموقع
اتصل بنا
- إذا كانت لديك أسئلة، يرجى الاتصال بنا، وسيتم الرد على جميع الأسئلة
- البريد الإلكتروني : David@tmaxcn.com
- البريد الإلكتروني : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- إضافة : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
المنتجات الساخنة
مدونة
LiIon Battery Tester
A Liion battery tester is a specialized device used to evaluate the performance, safety, and reliability of lithiumion batteries. These testers simulate realworld conditions and measure key parameters such as voltage, current, capacity, internal resistance, and temperature. By ensuring that Liion batteries meet their design specifications, these testers play a critical role in the development, manufacturing, and quality control of batteries for various applications.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of Liion battery testers.
●Design and Operation of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Key Components
Power Supply: Provides controlled voltage or current to charge or discharge the battery.
Measurement System: Measures voltage, current, temperature, and other parameters during testing.
Control Unit: Manages test sequences, adjusts parameters dynamically, and records data.
Safety Features: Prevents overcharging, overdischarging, short circuits, or thermal runaway during testing.
User Interface: Allows users to configure tests, monitor results, and analyze data.
2. Operation Principle
The tester applies controlled charging and discharging cycles to the battery under test.
It measures the battery's response, including its capacity, efficiency, internal resistance, and thermal behavior.
Advanced testers can simulate realworld operating conditions, such as varying temperatures, loads, and duty cycles.
●Functionalities of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Capacity Testing:
Measures the total energy a battery can store and deliver under specific conditions.
2. Cycle Life Testing:
Evaluates how many chargedischarge cycles a battery can endure before its capacity degrades significantly.
3. Internal Resistance Measurement:
Determines the resistance within the battery, which affects its efficiency and performance.
4. Safety Testing:
Simulates fault conditions (e.g., overcharging, short circuits) to ensure the battery remains safe.
5. StateofCharge (SOC) and StateofHealth (SOH) Estimation:
Calculates the remaining charge and overall health of the battery.
6. Temperature Monitoring:
Tracks the battery's thermal behavior to prevent overheating or thermal runaway.
●Advantages of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Comprehensive Testing:
Covers all key aspects of battery performance, ensuring reliable results across various conditions.
2. Reproducibility:
Enables consistent testing across multiple units, reducing variability in results.
3. CostEffectiveness:
Identifies defects early in the development process, minimizing costly redesigns or recalls.
4. Customizability:
Configurable settings allow testing tailored to specific battery chemistries and applications.
5. Safety Assurance:
Ensures the battery can handle fault conditions safely, protecting both the device and users.
●Challenges in Using LiIon Battery Testers
1. Complexity:
Modern Liion batteries are highly complex, requiring advanced testing equipment and expertise.
2. Simulation Accuracy:
Achieving realistic simulation of all possible operating conditions can be challenging.
3. TimeConsuming:
Comprehensive testing, especially for cycle life, may require extended periods.
4. Cost:
Highend battery testers can be expensive, particularly for smallscale developers.
5. Software Integration:
Ensuring seamless integration with battery management systems (BMS) and firmware can be difficult.
●Innovations in LiIon Battery Testing
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. RealTime Simulation:
Advanced signal generators provide dynamic, realtime simulations of battery behavior.
2. AIPowered Analytics:
Machine learning algorithms analyze test data to identify trends and predict potential issues.
3. Modular Designs:
Flexible configurations allow users to adapt the tester to different battery types and sizes.
4. Wireless Connectivity:
IoTenabled systems facilitate remote monitoring and control of testing processes.
5. Energy Efficiency:
Regenerative testing systems recover energy during discharge cycles, reducing power consumption.
●Applications of LiIon Battery Testers
Liion battery testers are widely used in various industries:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Ensuring the reliability and safety of EV batteries to maximize range and lifespan.
2. Consumer Electronics:
Testing batteries in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices for efficient power management.
3. Renewable Energy Storage:
Validating battery performance in largescale energy storage systems for grid stability.
4. Aerospace and Defense:
Ensuring robust battery performance in critical applications like satellites and military vehicles.
5. Medical Devices:
Verifying the safety and reliability of batteries in lifesaving medical equipment.
●The Future of LiIon Battery Testing
As battery technology continues to advance, Liion battery testers will become even more sophisticated. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize testing workflows and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become standard.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Combining battery testing with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics.
4. Development of New Battery Chemistries:
Adapting testers to accommodate nextgeneration batteries, such as solidstate or lithiumsulfur.
5. Global Standards Compliance:
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international standards for battery safety and performance.
●Conclusion
Liion battery testers are essential tools for ensuring the performance, safety, and reliability of lithiumion batteries. Their ability to simulate realworld conditions and measure critical parameters makes them indispensable in industries ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy.
December 12,2025.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
LiIon Battery Tester: Ensuring Performance and Safety
A Liion battery tester is a specialized device used to evaluate the performance, safety, and reliability of lithiumion batteries. These testers simulate realworld conditions and measure key parameters such as voltage, current, capacity, internal resistance, and temperature. By ensuring that Liion batteries meet their design specifications, these testers play a critical role in the development, manufacturing, and quality control of batteries for various applications.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of Liion battery testers.
●Design and Operation of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Key Components
Power Supply: Provides controlled voltage or current to charge or discharge the battery.
Measurement System: Measures voltage, current, temperature, and other parameters during testing.
Control Unit: Manages test sequences, adjusts parameters dynamically, and records data.
Safety Features: Prevents overcharging, overdischarging, short circuits, or thermal runaway during testing.
User Interface: Allows users to configure tests, monitor results, and analyze data.
2. Operation Principle
The tester applies controlled charging and discharging cycles to the battery under test.
It measures the battery's response, including its capacity, efficiency, internal resistance, and thermal behavior.
Advanced testers can simulate realworld operating conditions, such as varying temperatures, loads, and duty cycles.
●Functionalities of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Capacity Testing:
Measures the total energy a battery can store and deliver under specific conditions.
2. Cycle Life Testing:
Evaluates how many chargedischarge cycles a battery can endure before its capacity degrades significantly.
3. Internal Resistance Measurement:
Determines the resistance within the battery, which affects its efficiency and performance.
4. Safety Testing:
Simulates fault conditions (e.g., overcharging, short circuits) to ensure the battery remains safe.
5. StateofCharge (SOC) and StateofHealth (SOH) Estimation:
Calculates the remaining charge and overall health of the battery.
6. Temperature Monitoring:
Tracks the battery's thermal behavior to prevent overheating or thermal runaway.
●Advantages of LiIon Battery Testers
1. Comprehensive Testing:
Covers all key aspects of battery performance, ensuring reliable results across various conditions.
2. Reproducibility:
Enables consistent testing across multiple units, reducing variability in results.
3. CostEffectiveness:
Identifies defects early in the development process, minimizing costly redesigns or recalls.
4. Customizability:
Configurable settings allow testing tailored to specific battery chemistries and applications.
5. Safety Assurance:
Ensures the battery can handle fault conditions safely, protecting both the device and users.
●Challenges in Using LiIon Battery Testers
1. Complexity:
Modern Liion batteries are highly complex, requiring advanced testing equipment and expertise.
2. Simulation Accuracy:
Achieving realistic simulation of all possible operating conditions can be challenging.
3. TimeConsuming:
Comprehensive testing, especially for cycle life, may require extended periods.
4. Cost:
Highend battery testers can be expensive, particularly for smallscale developers.
5. Software Integration:
Ensuring seamless integration with battery management systems (BMS) and firmware can be difficult.
●Innovations in LiIon Battery Testing
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. RealTime Simulation:
Advanced signal generators provide dynamic, realtime simulations of battery behavior.
2. AIPowered Analytics:
Machine learning algorithms analyze test data to identify trends and predict potential issues.
3. Modular Designs:
Flexible configurations allow users to adapt the tester to different battery types and sizes.
4. Wireless Connectivity:
IoTenabled systems facilitate remote monitoring and control of testing processes.
5. Energy Efficiency:
Regenerative testing systems recover energy during discharge cycles, reducing power consumption.
●Applications of LiIon Battery Testers
Liion battery testers are widely used in various industries:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Ensuring the reliability and safety of EV batteries to maximize range and lifespan.
2. Consumer Electronics:
Testing batteries in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices for efficient power management.
3. Renewable Energy Storage:
Validating battery performance in largescale energy storage systems for grid stability.
4. Aerospace and Defense:
Ensuring robust battery performance in critical applications like satellites and military vehicles.
5. Medical Devices:
Verifying the safety and reliability of batteries in lifesaving medical equipment.
●The Future of LiIon Battery Testing
As battery technology continues to advance, Liion battery testers will become even more sophisticated. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize testing workflows and reduce human intervention.
2. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and energyefficient designs will become standard.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Combining battery testing with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics.
4. Development of New Battery Chemistries:
Adapting testers to accommodate nextgeneration batteries, such as solidstate or lithiumsulfur.
5. Global Standards Compliance:
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international standards for battery safety and performance.
●Conclusion
Liion battery testers are essential tools for ensuring the performance, safety, and reliability of lithiumion batteries. Their ability to simulate realworld conditions and measure critical parameters makes them indispensable in industries ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy.
What excites you most about the role of Liion battery testers in advancing battery technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative tools can shape the future of energy storage and mobility.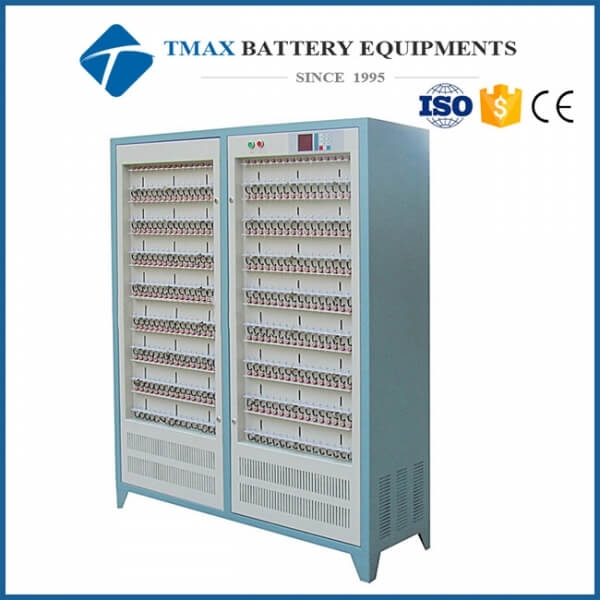
 English▼
English▼




 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

