مدونة الموقع
اتصل بنا
- إذا كانت لديك أسئلة، يرجى الاتصال بنا، وسيتم الرد على جميع الأسئلة
- البريد الإلكتروني : David@tmaxcn.com
- البريد الإلكتروني : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- إضافة : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
المنتجات الساخنة
مدونة
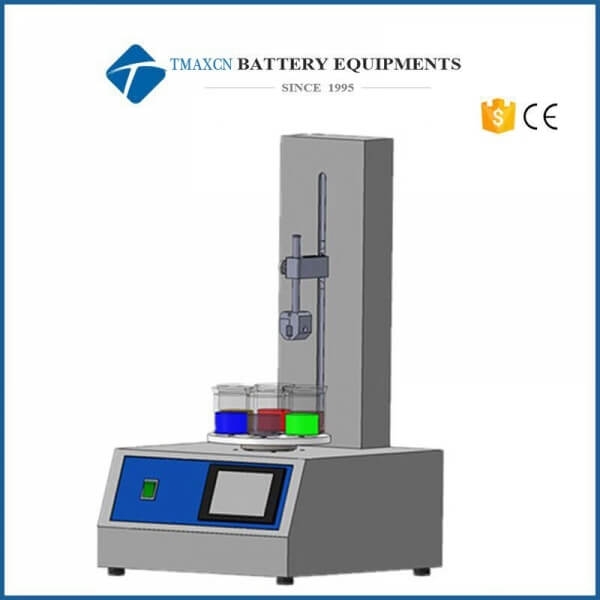
Dip Coater
A dip coater is a device used to apply thin, uniform coatings onto substrates by immersing them in a liquid solution and then withdrawing them at a controlled speed. This technique, known as dip coating, is widely employed in industries such as electronics, optics, solar energy, and biomedical applications due to its simplicity, costeffectiveness, and ability to produce highquality thin films.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of dip coaters.
●Design and Operation of Dip Coaters
1. Key Components
Coating Solution Reservoir: Holds the liquid solution containing the material to be deposited.
Substrate Holder: Secures the substrate during immersion and withdrawal.
Motorized System: Controls the vertical movement of the substrate with precise speed and position.
Control Unit: Monitors and adjusts parameters such as dipping speed, withdrawal speed, and dwell time.
2. Operation Principle
The substrate is immersed into the coating solution for a specific duration (dwell time).
It is then withdrawn from the solution at a controlled speed, allowing the liquid film to spread evenly across the surface.
As the solvent evaporates, a thin solid layer forms on the substrate.
●Functionalities of Dip Coaters
1. Thin Film Deposition:
Produces uniform coatings with thicknesses ranging from nanometers to micrometers.
2. LayerbyLayer Assembly:
Enables the sequential deposition of multiple layers for complex structures.
3. Surface Modification:
Alters the surface properties of substrates for specific applications (e.g., hydrophobicity or conductivity).
4. Scalability:
Suitable for both laboratoryscale experiments and industrial production.
●Advantages of Dip Coaters
1. CostEffectiveness:
Simple setup and minimal material waste compared to other coating techniques.
2. Uniformity:
Provides consistent film thickness over large areas.
3. Versatility:
Compatible with a wide range of materials, including polymers, ceramics, metals, and composites.
4. Precision Control:
Adjustable parameters (speed, dwell time, angle) allow finetuning of film properties.
5. Scalability:
Easily adaptable for scaling up from labscale research to industrial manufacturing.
●Challenges in Using Dip Coaters
1. Film Thickness Sensitivity:
Film thickness depends on several factors, including withdrawal speed, solution concentration, and viscosity, requiring careful optimization.
2. Drying Conditions:
Evaporation rate and ambient conditions can affect film quality and uniformity.
3. Edge Effects:
Uneven coating may occur at the edges of the substrate due to capillary forces.
4. Particle Contamination:
Particles in the solution can cause defects in the deposited film.
5. Complex Geometries:
Difficult to coat nonflat or irregularly shaped substrates uniformly.
●Innovations in Dip Coaters
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating advanced technologies:
1. Automated Control Systems:
Programmable controls for precise parameter adjustments and unattended operation.
2. Environmental Chambers:
Controlled atmospheres to optimize drying conditions and reduce contamination.
3. RealTime Monitoring:
Sensors and data analytics tools for continuous monitoring of coating processes.
4. Improved Reservoir Designs:
Advanced reservoirs minimize particle settling and ensure uniform solution distribution.
5. MultiAxis Motion:
Capability to coat substrates at angles or with rotational motion for complex geometries.
●Applications of Dip Coaters
Dip coaters are used in a variety of industries and research fields:
1. Optics:
Production of antireflective, hydrophobic, or conductive coatings for lenses, mirrors, and displays.
2. Solar Energy:
Fabrication of photovoltaic cells and transparent conductive films.
3. Electronics:
Deposition of dielectric, insulating, or semiconducting layers for microelectronics.
4. Biomedical:
Coating of medical devices, implants, and biosensors with biocompatible or functional materials.
5. Ceramics and Composites:
Manufacturing of ceramic coatings and layered composite structures.
●The Future of Dip Coaters
As technology advances, dip coaters will continue to evolve to meet the demands of emerging applications. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize coating processes and reduce human intervention.
2. Customization Options:
Modular designs will allow users to tailor coaters for specific materials and applications.
3. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and reduced solvent use will become integral parts of future systems.
4. Integration with Advanced Technologies:
IoTenabled coaters will connect to smart labs for realtime data analysis and process optimization.
5. Development of New Materials:
Advances in nanomaterials and composites will drive innovation in coating formulations and applications.
●Conclusion
Dip coaters are essential tools for thin film deposition, offering simplicity, precision, and versatility in a wide range of applications. Their ability to produce uniform coatings with controlled thickness makes them indispensable in industries such as optics, electronics, and renewable energy.
November 11,2025.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
Dip Coater: A Versatile Tool for Thin Film Deposition
A dip coater is a device used to apply thin, uniform coatings onto substrates by immersing them in a liquid solution and then withdrawing them at a controlled speed. This technique, known as dip coating, is widely employed in industries such as electronics, optics, solar energy, and biomedical applications due to its simplicity, costeffectiveness, and ability to produce highquality thin films.
In this article, we will explore the design, operation, advantages, challenges, and applications of dip coaters.
●Design and Operation of Dip Coaters
1. Key Components
Coating Solution Reservoir: Holds the liquid solution containing the material to be deposited.
Substrate Holder: Secures the substrate during immersion and withdrawal.
Motorized System: Controls the vertical movement of the substrate with precise speed and position.
Control Unit: Monitors and adjusts parameters such as dipping speed, withdrawal speed, and dwell time.
2. Operation Principle
The substrate is immersed into the coating solution for a specific duration (dwell time).
It is then withdrawn from the solution at a controlled speed, allowing the liquid film to spread evenly across the surface.
As the solvent evaporates, a thin solid layer forms on the substrate.
●Functionalities of Dip Coaters
1. Thin Film Deposition:
Produces uniform coatings with thicknesses ranging from nanometers to micrometers.
2. LayerbyLayer Assembly:
Enables the sequential deposition of multiple layers for complex structures.
3. Surface Modification:
Alters the surface properties of substrates for specific applications (e.g., hydrophobicity or conductivity).
4. Scalability:
Suitable for both laboratoryscale experiments and industrial production.
●Advantages of Dip Coaters
1. CostEffectiveness:
Simple setup and minimal material waste compared to other coating techniques.
2. Uniformity:
Provides consistent film thickness over large areas.
3. Versatility:
Compatible with a wide range of materials, including polymers, ceramics, metals, and composites.
4. Precision Control:
Adjustable parameters (speed, dwell time, angle) allow finetuning of film properties.
5. Scalability:
Easily adaptable for scaling up from labscale research to industrial manufacturing.
●Challenges in Using Dip Coaters
1. Film Thickness Sensitivity:
Film thickness depends on several factors, including withdrawal speed, solution concentration, and viscosity, requiring careful optimization.
2. Drying Conditions:
Evaporation rate and ambient conditions can affect film quality and uniformity.
3. Edge Effects:
Uneven coating may occur at the edges of the substrate due to capillary forces.
4. Particle Contamination:
Particles in the solution can cause defects in the deposited film.
5. Complex Geometries:
Difficult to coat nonflat or irregularly shaped substrates uniformly.
●Innovations in Dip Coaters
To address these challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating advanced technologies:
1. Automated Control Systems:
Programmable controls for precise parameter adjustments and unattended operation.
2. Environmental Chambers:
Controlled atmospheres to optimize drying conditions and reduce contamination.
3. RealTime Monitoring:
Sensors and data analytics tools for continuous monitoring of coating processes.
4. Improved Reservoir Designs:
Advanced reservoirs minimize particle settling and ensure uniform solution distribution.
5. MultiAxis Motion:
Capability to coat substrates at angles or with rotational motion for complex geometries.
●Applications of Dip Coaters
Dip coaters are used in a variety of industries and research fields:
1. Optics:
Production of antireflective, hydrophobic, or conductive coatings for lenses, mirrors, and displays.
2. Solar Energy:
Fabrication of photovoltaic cells and transparent conductive films.
3. Electronics:
Deposition of dielectric, insulating, or semiconducting layers for microelectronics.
4. Biomedical:
Coating of medical devices, implants, and biosensors with biocompatible or functional materials.
5. Ceramics and Composites:
Manufacturing of ceramic coatings and layered composite structures.
●The Future of Dip Coaters
As technology advances, dip coaters will continue to evolve to meet the demands of emerging applications. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will optimize coating processes and reduce human intervention.
2. Customization Options:
Modular designs will allow users to tailor coaters for specific materials and applications.
3. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and reduced solvent use will become integral parts of future systems.
4. Integration with Advanced Technologies:
IoTenabled coaters will connect to smart labs for realtime data analysis and process optimization.
5. Development of New Materials:
Advances in nanomaterials and composites will drive innovation in coating formulations and applications.
●Conclusion
Dip coaters are essential tools for thin film deposition, offering simplicity, precision, and versatility in a wide range of applications. Their ability to produce uniform coatings with controlled thickness makes them indispensable in industries such as optics, electronics, and renewable energy.
What excites you most about the role of dip coaters in advancing thin film technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative tools can shape the future of material science and engineering.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

